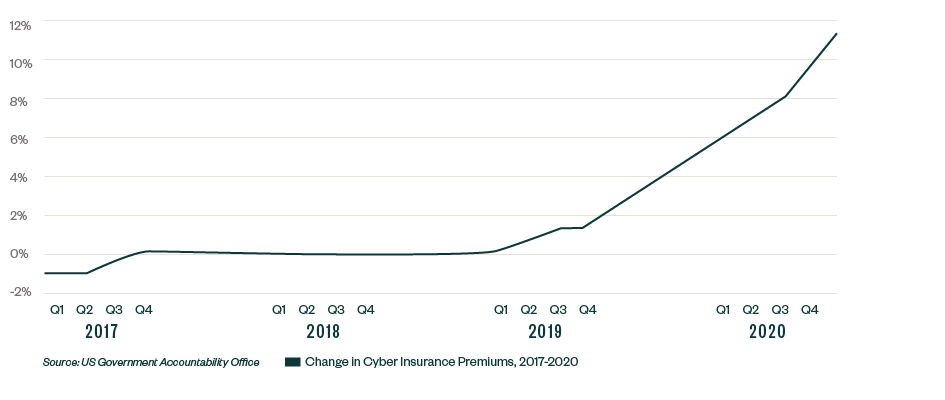
One of the most important components of managing cyber-risk is prevention. Some organizations, however, sometimes fail to realize that data breaches can cost more than just lost data or access to systems.
The consequences of a cyberbreach can affect various business relationships — insurance companies, banking institutions, investors, or potential buyers, for example. The implications of those intangible costs often mean companies must adhere to criteria that helps them evaluate the security of companies.
There’s no right or wrong way to secure an organization. Each solution should be unique to the structure of the company, the audience you serve, and the type of data you manage. The goal is to strengthen your technology infrastructure to build confidence in your business.
The consequences of a cyberbreach can affect various business relationships — insurance companies, banking institutions, investors, or potential buyers, for example.
What are the financial costs of a data breach?
The average cost of a data breach is $3.86 million, which is a conservative number, according to the Ponemon Institute. Some breaches go unreported because companies don’t want to damage their reputation or lose client trust.
The average life cycle of a breach is 280 days, from identification to containment. During that time, there are costs an organization needs to account for.