If your organization is using a governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) tool, you’ll see the greatest efficiency and impact when your audit team understands how to work within that platform.
Requirements like SOC 2, HIPAA, and FedRAMP demand significant documentation and control validation — tasks GRC tools can help streamline through automation and centralized data. Pairing that technology with an auditor who’s familiar with the tool’s workflows can reduce friction, improve accuracy, and help your team move through compliance faster.
Discover how combining GRC tools with a knowledgeable auditor can elevate your audit compliance management processes with the following insights.
GRC tools simplify the audit process
Compliance auditors evaluate whether an organization meets internal policies, regulatory requirements, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX), HIPAA, or GDPR, and industry standards like ISO 27001 or NIST. GRC tools support this work by centralizing control libraries, streamlining evidence collection, and standardizing workflows and documentation.
Working with an auditor who understands how to align with and leverage GRC platforms can help streamline the audit process. This collaboration enables real-time visibility into security controls, supports proactive risk management, and facilitates timely remediation.
In addition to providing data to your auditor, there are also benefits for your organization. A GRC tool can enhance your ability to self-assess, organize documentation, and curate evidence.
Our teams are trained to navigate the leading GRC automation tools. Our firm is one of the few CPA firms validated as assessors for key frameworks, including a SOC examination, PCI DSS, HITRUST CSF, HIPAA, FedRAMP, NIST, and CSA STAR services.
How auditors use data from GRC tools
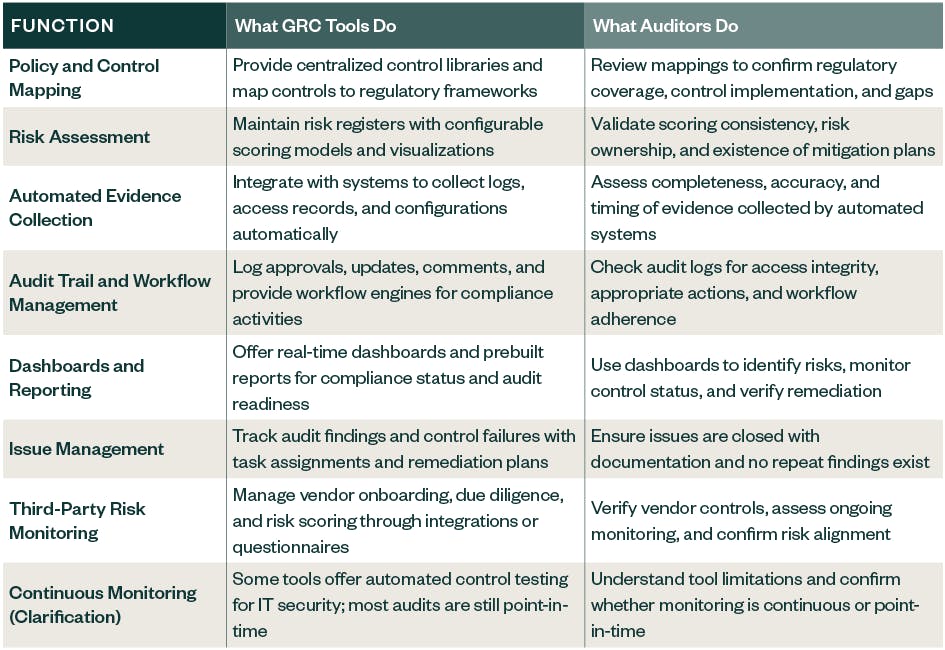
GRC tools streamline and enhance the audit process by centralizing data, standardizing workflows, and enabling real-time visibility into risk and control performance.
However, it’s important to note that your auditor shouldn’t only rely on a GRC tool’s output. Those results are a useful starting part, but there are still checks and controls to verify and assess the data during your organization’s audit process.
The table below outlines how these tools function across key areas of compliance and how auditors engage with them to support oversight and maintain regulatory alignment.
Workflow: GRC tool to auditor
How to select an auditor trained in GRC tools
For a more efficient and effective compliance experience, there are three main considerations when choosing an auditor with GRC tool training:
- Select an auditor with proven experience in the specific GRC platforms your organization currently uses or intends to implement
- Understand the auditor’s philosophy regarding the integration of technology into their audit approach — this can impact the effectiveness of the compliance process
- Confirm that the auditor’s methodology is well-suited to the capabilities and workflows of your selected GRC tool
Once you’ve chosen an auditor, communication between your internal team, the auditor, and the GRC tool provider becomes the key component for a successful implementation. This not only enhances transparency but also aligns all parties’ objectives.

